Secure Maximum Compensation for Your Georgia Traumatic Brain Injury Claim After a Car Accident
Key Points:
- If you suffered a traumatic brain injury due to an accident, any related costs or lifestyle changes should be considered within your settlement compensation.
- Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs) can cause permanent, life-altering changes that affect your physical, cognitive, and sensory functions.
- A car accident lawyer who specializes in personal injury may help you get full and fair compensation for the harm caused by your accident.
Table of Contents
Understanding Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs) in Car Accidents
TBIs are among the most serious consequences of car accidents, potentially leading to life-altering changes in brain function and quality of life. Here’s a breakdown of the primary ways you can get a TBI in a car accident:
- Direct Impact: During a collision, your head might collide with objects within the car, such as the dashboard, steering wheel, or side windows.
- Rapid Acceleration or Deceleration: A sudden halt or thrust can cause your brain to shift within the cerebrospinal fluid of your skull, causing your brain to impact both the point of collision and the exact opposite side within the skull.
- Objects Penetrating Skull: Although less frequent, these injuries occur when external objects like shattered glass or accident debris penetrate your skull and affect the brain tissue.
- Rotational Movements: Intense rotational forces resulting from varying movement speeds of different brain parts during the accident can lead to the tearing of your brain’s internal structures.
- Increased Intracranial Pressure: Elevated pressure within the skull can contribute to brain damage.
- Secondary Injuries: Some injuries can manifest over time following the primary trauma.
While safety innovations like seat belts, airbags, and advanced vehicular design have significantly reduced TBI severity in car accidents, they cannot reduce all of the risks. If you’ve been in a car accident, consulting a medical professional about potential head injuries is crucial, even if symptoms are not immediately apparent. Early intervention can significantly improve your recovery outcomes.
Summary of TBIs in Car Accidents:
- There are multiple ways you can get a TBI in a car accident, including some injuries that occur long after the initial accident.
- Wearing your seatbelt is key to helping lessen your chances of receiving a TBI.
- Always consult with your doctor if you suspect a head injury following an accident.
What Is Classified as a Traumatic Brain Injury?

A TBI occurs when there is a violent blow or jolt to the head or body, or when an object penetrates the skull. Here’s a breakdown of what classifies as a TBI:
- Severity:
- Mild TBI (mTBI): Often referred to as a concussion, involves brief or no loss of consciousness (under 30 minutes) and temporary symptoms.
- Moderate TBI: Involves loss of consciousness from 30 minutes to 24 hours, with symptoms lasting weeks to months.
- Severe TBI: Involves loss of consciousness for more than 24 hours, with potential permanent impairments or life-threatening complications.
- Secondary Changes: These are not immediate injuries but changes that evolve over hours to days after the primary injury. They can include brain swelling, increased intracranial pressure, seizures, or infections.
- It is essential to note that the brain is complex, so your outcome and recovery may vary greatly depending on the severity and location of the injury, as well as your overall health. Even mTBIs, like concussions, should be taken seriously and monitored closely to ensure optimal recovery.
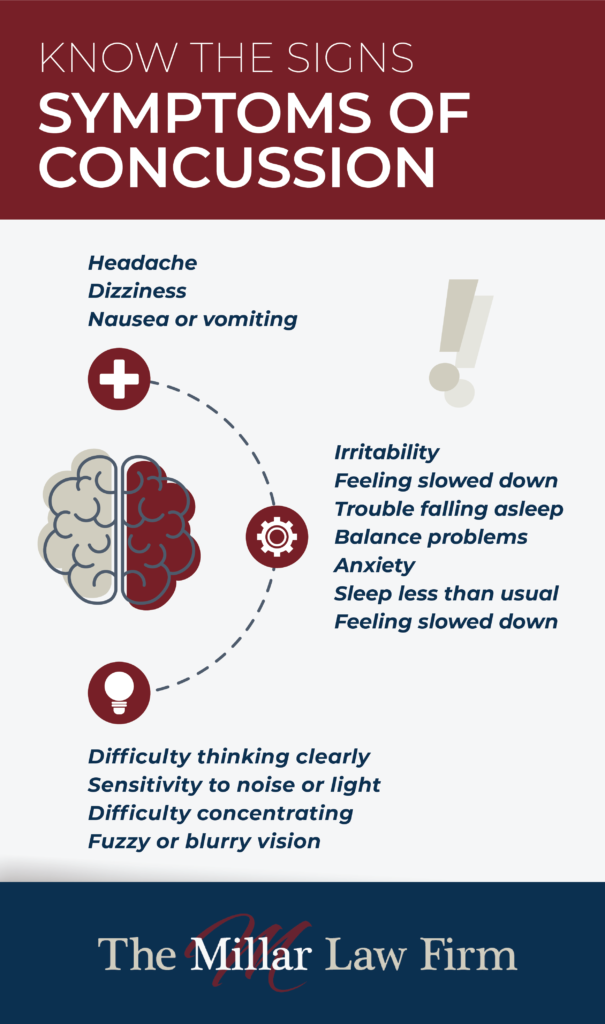
- Symptoms of a Traumatic Brain Injury
- A TBI can have a full range of physical and sensory symptoms, which depend on the severity of the injury. Symptoms can sometimes develop immediately after the traumatic event, while others may appear as time passes, showing days or even weeks later.
- Symptoms of a mild brain injury (concussion):
- Less severe brain injuries are often referred to as a mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI), the most common of which is a concussion. Symptoms of a concussion can include:
- Brief loss of consciousness after the injury
- Memory problems or amnesia surrounding the traumatic event
- Dizziness or “seeing stars”
- Ringing in the ears
- Nausea
- Fatigue and sleep disturbances
- Confusion
- Sensitivity to light or noise
- Mood changes
- The term “mild” can be misleading. It only refers to the initial presentation and immediate aftermath of the injury, not necessarily the potential long-term effects or seriousness. While some people with concussions recover fully within a few days or weeks, others might experience symptoms that persist for months or longer; this condition is sometimes referred to as post-concussion syndrome.
Symptoms of moderate-to-severe traumatic brain injury:
In more severe traumatic brain injuries, the above symptoms may develop along with more dramatic signs of damage, including:
- Loss of consciousness for several minutes to hours
- Convulsions or seizures
- One or both eye pupils may appear expanded or dilated
- Clear fluid drainage from the nose or ears
- Numbness or unresponsiveness in the fingers and toes
- Physical coordination impairments
- Profound confusion
- Agitation or combativeness
- Slurred speech
TBI Can Alter a Victim’s State of Consciousness
Head trauma can cause prolonged or permanent changes in a person’s state of consciousness, responsiveness, and awareness.
When severe TBI occurs, it can result in the following impaired states of brain function, including:
- Minimal consciousness: They may show some signs of self and environmental awareness, such as establishing eye contact, holding objects, responding to commands, and having limited verbal responses.
- Vegetative state: They lack self or environmental awareness; however, they may exhibit eye twitching or movements, make sounds, respond to reflexes, or move. It is possible that a vegetative state can become permanent, but sometimes individuals progress to a minimally conscious state.
- Coma: They are unconscious, unaware of their surroundings, and unable to respond to any stimulus. Depending on the severity of injuries, a coma can last days, weeks, or months. A comatose patient may emerge from a coma or enter a vegetative state.
- Brain death: When a person is declared brain dead, there is no measurable activity in their brain or brainstem. In this state, removing breathing devices will cause their breathing to cease and heart failure to follow. Brain death is considered irreversible.
Accidents That Can Cause a Traumatic Brain Injury
In addition to vehicular accidents, any impact to the head or skull can cause a TBI, including:
- Slips and falls: Falls from a ladder, stairs, in the bath, and at public places are the most common causes of traumatic brain injury. Older adults and young children are often the victims of these types of accidents.
- Sports injuries: Traumatic brain injuries may be caused by accidents from sports, including soccer, boxing, football, baseball, lacrosse, skateboarding, hockey, and other high-impact or extreme activities. These are particularly common when youth are unsupervised, failing to wear proper protective gear, or when protective equipment is defective.
- Work-related injuries: Workplaces where hazardous or slippery conditions occur may have a high likelihood of accidents that result in TBI. Careers involving combat or the use of explosives present significant hazards.
- Other incidents: Criminal behavior, such as gunshot wounds, domestic violence, child abuse, and other assaults, can also cause TBI. Shaken baby syndrome is also a traumatic brain injury that is caused by the violent shaking of infants.
A TBI Case Study: The Price of Distraction - Sarah's Story
Elementary school teacher Sarah Collins (name changed to protect her privacy) was rear-ended in stopped in traffic on I-85 by a marketing executive who was distracted by texting. Under Georgia's Hands-Free Act, the Executive's actions constituted negligence per se, meaning as a matter of law.
The force of the violent impact caused Sarah's brain to impact against the back and front of her skull, as her brain moved back and forth inside of her head - a typical reaction in a moderate to large rear-end hit. As a result, Sarah suffered a moderate traumatic brain injury. After blacking out, she awoke to a dramatically different life. Sarah struggled with slurred speech, memory problems, and poor concentration. Before her accident, Sarah's co-workers knew her as cheerful, quick witted, and creative in the classroom. But Sarah could never return to teaching. Her medical expenses exceeded $100,000 and she will need future cognitive therapy.
The insurance company fought the claim, arguing that based on a history of migraines, the last of which was several years before the accident, Sarah was faking or exaggerating her condition. However, working closely with her neurologist, our Firm was able to demonstrate that her symptoms were proximately caused by the accident, and the case settled for the limits of the Executive's liability insurance policy and Sarah's underinsured motorist coverage.
Treating Traumatic Brain Injuries
If you have a TBI, your doctor will first ensure you are stable, meaning that you have enough oxygen absorption and a healthy blood pressure. Here’s how they will treat you based on diagnosis:
- mTBI (or concussion): Pain relievers for any headaches and ample rest. Monitor symptoms to ensure they do not worsen.
- Moderate to severe TBI: Expect a hospital stay for observation. Some cases may require surgery to remove blood clots or repair skull fractures. Depending on symptoms, you may be given different medications to aid with recovery.
Rehabilitation following initial treatments is crucial as it can help your brain and body return to a normal state. Here are common forms of rehabilitation:
- Physical therapy for movement
- Speech therapy to help with speech impediments
- Therapies to assist with daily tasks and thinking
Depending on the severity of your injury, you might need long-term care to help you live your best life, which could involve continued therapy and counseling, or support groups.
TBI Can Be a Permanent Condition
Because the brain is still not fully understood, it’s challenging for doctors to predict how permanent TBI will be and how it may impact your life.
In some circumstances, you can expect a full recovery following an accident.Your brain can often find ways to re-route information, skills, and memories, so there are no permanent effects. Other times, your injuries may remain permanent, and the damage will hinder certain functions for the rest of your life.
Seeking Compensation for Your Injuries
If someone else’s negligence caused your traumatic brain injury, you can recover compensation for those injuries and the effects they’ve had on your life, including:
- All related medical expenses and treatments since the accident, including emergency care, hospitalization, rehabilitation therapy, medication, medical equipment, and in-home care services. For long-term or permanent injuries, you can pursue compensation for future medical needs based on expert medical projections and life-care planning assessments.
- Recouping lost wages. This can also include future lost wages if you cannot return to your job because of your injuries.
- Your pain and suffering, including a loss of your usual quality of life. If your everyday activities are negatively impacted, you can usually expect compensation to help adjust for a lessened quality of life.
While it can be difficult to quantify the many losses a TBI victim experiences, these circumstances should all be factored into a full and fair settlement and can affect the time it takes to settle the case.
Frequently Asked Questions About Traumatic Brain Injury Cases in Atlanta
Do I need a lawyer for a traumatic brain injury after a car accident?
Yes, hiring an experienced traumatic brain injury lawyer in Atlanta is critical. TBI cases often involve complex medical evidence and significant compensation for long-term care, lost income, and emotional suffering. A qualified attorney can fight for the full compensation you deserve.
How much compensation can I recover for a traumatic brain injury?
Compensation varies based on the severity of your injury, your medical expenses, lost wages, and the long-term impact on your life. In Atlanta, settlements for traumatic brain injuries can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars. Due to the severity and potential value of a TBI case, in addition to reporting your injury to the at-fault driver, we recommend that you notify your underinsured motorist carrier and apply for any med-pay benefits that your policy may include.
How long do I have to file a traumatic brain injury lawsuit in Georgia?
In Georgia, the statute of limitations for personal injury claims, including traumatic brain injuries, is generally two years from the date of the accident. Some exceptions may apply, therefore, consult with an attorney as soon as possible.
What if my TBI symptoms appear days after the accident?
It is not uncommon for TBI symptoms to be delayed. Even if symptoms arise later, you may still be entitled to compensation. Seek medical attention immediately and consult a traumatic brain injury lawyer in Atlanta to protect your case.
What makes your law firm different when handling TBI cases?
Our firm has extensive experience handling traumatic brain injury cases in Atlanta. We work closely with medical experts, gather detailed evidence, and aggressively advocate for maximum recovery on behalf of our clients.
Consult With a Personal Injury Lawyer for Answers
Because it can be challenging to get a fair settlement following a TBI, it’s crucial to look for an Atlanta law firm that handles these matters regularly. Here’s what you can expect from a personal injury lawyer at The Millar Law Firm:
- Receive a free first consultation to learn how we can best help you. Our team will provide a full picture of what your future expenses may look like and explain your options to protect yourself and your family.
- They will use their expertise to address unforeseen losses such as long-lasting care and expenses resulting from a permanent disability.
- They will gather adequate proof of your injury and the attendant impacts, including medical records, work history, and witness statements.

 1201 West Peachtree Street #2339 Atlanta, GA 30309+1-770-212-3795$0-$100000
1201 West Peachtree Street #2339 Atlanta, GA 30309+1-770-212-3795$0-$100000Kelly Buchanan is highly professional, detail-oriented, and delivers outstanding customer service. She consistently follows up and prioritizes her clients' best interests. I would confidently recommend the Millar Law Firm to anyone in need of Legacy services.