Key Points:
- Common signs of a concussion include headache, nausea, ringing in the ears, fatigue, blurred vision, confusion, memory issues, dizziness, and slurred speech.
- Symptoms that may appear later include difficulty concentrating, personality changes, sensitivity to light and noise, changes in sleep patterns, psychological changes, and changes in taste and smell.
- In children, concussion symptoms can include appearing dazed, irritability, loss of balance, crying more than usual, changes in eating or sleeping patterns, and seizures.
- If you have suffered a concussion following a Georgia car, truck or motorcycle accident, an experienced personal injury lawyer can help you recover the compensation you need by carefully evaluating your case and obtaining the medical evidence needed to win your case.
If you’ve been in an accident, seeing a doctor as soon as possible is crucial. Even if you feel fine and don’t see any immediate injuries, hidden damage could emerge later. Brain injuries, in particular, can take hours or even days to manifest. While not all brain injuries are severe or fatal, untreated ones can lead to permanent, life-altering damage.
Doctors have the expertise to spot potential brain injuries and the necessary tools to diagnose and treat them. Additionally, a doctor’s report and diagnosis can be essential in proving your damages if you decide to pursue a legal claim for these injuries. Their expert, unbiased reports can serve as reliable evidence and witness testimony if needed.
Some victims may avoid medical help due to concerns about the cost of care. However, these expenses can be included in your insurance claim and settlement.
Questions That Can Help Your Doctor Detect a Concussion from a motor vehicle collision
Medical resources, including the Mayo Clinic and the Centers for Disease Control, list the following questions as reliable means to determine whether a concussion occurred.
- Did you lose consciousness? It’s a common misconception that loss of consciousness always occurs with brain injury. It does not and should not be considered a reliable diagnostic tool on its own.
- Was your head forcibly shaken due to the impact? A direct blow to the head can cause a concussion, but violent shaking can also cause the brain, which floats in fluid inside the skull, to collide with the skull, causing damage.
- Did your head make contact with anything? A violent impact can cause brain bruising.
- Did the airbags deploy and hit your head? While airbags are designed to save lives, their explosive deployment can also cause injury.
- Was the impact with the other vehicle significant? The force of the collision helps law enforcement assess the speed of the vehicles and the force inflicted upon the victims.
- Do you feel pain in your neck, upper back, face, or head? Such pain could indicate that muscles, tendons, and other soft tissues were stretched or strained during the impact.
- Are you experiencing any nausea or dizziness? Head trauma can cause loss of balance and make the world around you feel like it’s spinning. Nausea, dizziness, or ringing in the ears can indicate a brain injury.
- Do you remember everything? Memory loss is common with brain trauma. If you cannot recall names or specifics about the accident, your doctor may suspect head trauma.
- Are you having any sensitivity to noise or light? After a brain injury, it’s common to experience discomfort when exposed to bright light or loud noises.
- Do you have a headache following the accident? Lingering headaches after a head injury can vary in severity and duration. Your physician will evaluate these symptoms along with any others you may have.
What are the Common Signs or Symptoms of a Concussion?
The signs and symptoms of brain trauma and concussions can be subtle, and they don’t always show up immediately after an accident.
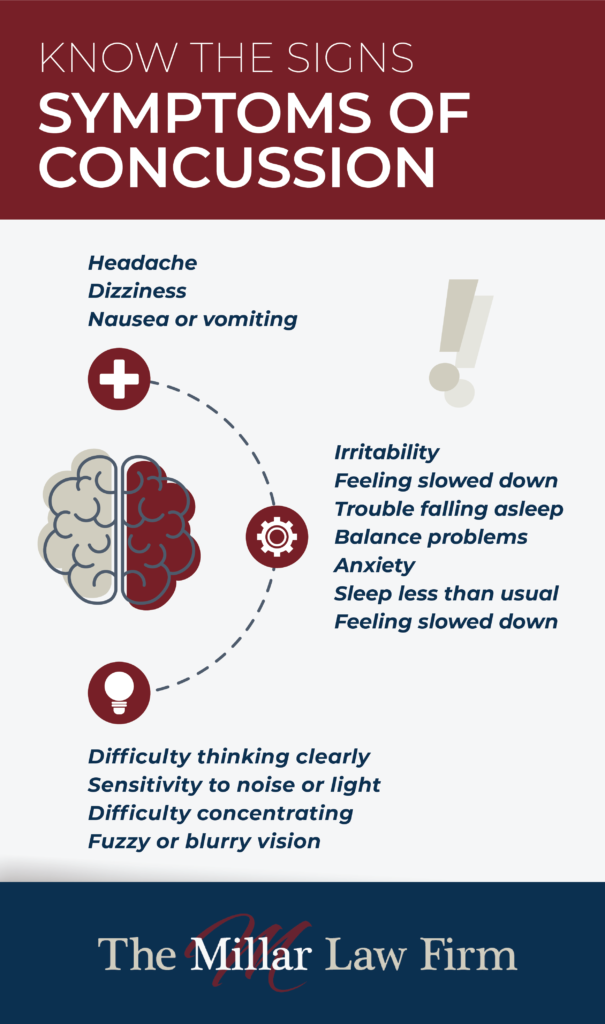
The following list includes some of the physical signs and symptoms of a concussion or traumatic brain injury:
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Ringing in the ears
- Fatigue or drowsiness
- Blurred vision
- Confusion or feeling dazed and “disconnected”
- Appearing to be dazed or confused
- Foggy recollection or no memory of the traumatic event
- Dizziness, ” seeing stars,” or having sparkling lights in your vision
- Temporary loss of consciousness following the event
- Slurred speech
- Slow response to questions
- Forgetfulness or repetition of questions or comments
Some of the slower-manifesting symptoms that may not appear until hours, days, or even weeks later are:
- Inability to concentrate
- Memory complaints
- Personality changes, such as unusual irritability
- Sensitivity to light and noise
- Changes in sleep patterns
- Psychological changes, such as depression
- Changes in taste and smell
What Are the Symptoms of a Concussion for a Child?
Head trauma is common in young children but can be challenging to diagnose since they often cannot describe how they feel. To identify a possible concussion in a child, watch for the following symptoms:
- Appearing dazed or confused
- Lethargy or tiring easily
- Irritability and crankiness
- Loss of balance or staggering while walking
- Crying more than usual
- Changes in eating or sleeping patterns
- Lack of interest in favorite toys
- Seizures
- Vomiting
How Do Medical Professionals Detect or Identify a Concussion?
When you see your physician, they will ask about many of the symptoms above to determine whether a brain injury is likely. In addition, the doctor will examine you and check the pupils of your eyes to see if they are dilated differently or unevenly, as this can be one of several tell-tale neurological signs of a concussion or other brain injury.
Your doctor may also order a computerized tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain to check medical problems that could be causing your symptoms. Both can be used to identify brain abnormalities, such as swelling, bruising, or bleeding, that might explain your symptoms.
Can a Concussion from a Car Accident Result in Death?
Yes, a concussion from a car accident can potentially result in death, though it’s rare. A concussion is a type of traumatic brain injury (TBI) caused by a blow or jolt to the head, disrupting normal brain function. Most people recover fully from mild concussions, but severe cases can lead to serious complications, including death.
Here are a few ways this can happen:
- Second Impact Syndrome: Imagine getting a second concussion before the first one has healed. This can cause rapid and severe brain swelling, which can be fatal. It’s like adding fuel to a fire that’s already burning.
- Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE): Repeated concussions can lead to CTE, a progressive brain disease. While CTE itself doesn’t directly cause death, it can lead to symptoms like depression and impulsive behavior, significantly increasing the risk of fatal outcomes. It’s a slow, dangerous spiral.
- Intracranial Hemorrhage: A concussion can cause bleeding in or around the brain. If this bleeding isn’t caught and treated quickly, it can lead to increased pressure inside the skull, brain damage, and death. Think of it like a ticking time bomb.
- Brain Swelling: Severe concussions can cause brain swelling, increasing pressure within the skull. If the pressure gets too high, it can cause brain damage and be life-threatening. It’s like over-inflating a balloon until it bursts.
So, if you or someone you know experiences a head injury, don’t take it lightly. Get medical attention immediately to assess the severity of the concussion and prevent any complications. Your brain is too important to take chances with!

 1201 West Peachtree Street #2339 Atlanta, GA 30309+1-770-212-3795$0-$100000
1201 West Peachtree Street #2339 Atlanta, GA 30309+1-770-212-3795$0-$100000The people that work here are professional and extremely helpful. They answered any questions I had and were very calculated throughout this entire process.

Does a Car Accident Lawyer Need to Prove That the Head Hit Something to Establish a Concussion?
No, a car accident lawyer does not need to prove that the head hit something to establish a concussion. Concussions can occur from a direct blow to the head or from violent shaking that causes the brain to move within the skull. For instance, in a car accident, the sudden jolt or whiplash effect can cause the brain to collide with the inside of the skull, resulting in a concussion. Therefore, proving a direct impact to the head is not necessary to establish that a concussion has occurred.
Instead, a car accident lawyer focuses on medical evidence and expert testimony to demonstrate the presence of a concussion. Medical records, doctor’s diagnoses, and neurological assessments can provide detailed information about the injury. Additionally, witness statements and the victim’s account of symptoms like dizziness, confusion, or headaches can support the claim. By gathering comprehensive evidence, the lawyer can effectively prove that a concussion occurred, even without direct head impact.
What is the Value of a Car Accident Case When the Only Injury is a Concussion?
The value of a car accident case when the only injury is a concussion can vary quite a bit. It really depends on a few key factors, including how severe the concussion is, how it impacts your daily life, your medical expenses, lost wages, and any long-term effects. For example, if the concussion is minor, the case might only be worth a few thousand dollars (if that). However, if it’s more serious and leads to ongoing medical treatment, time off work, or long-term cognitive or emotional issues, the compensation could be in the six-figure range.
A big part of the case value depends on the medical bills and how it changed the accident victims life. If the concussion requires significant medical attention and results in high medical expenses, the compensation will likely be higher. Additionally, the circumstances of the accident, such as who was at-fault and the insurance policy limits, also play a role. Because the brain is among the most critical organs in the body. If the concussion is life changing, it can be a 6 and maybe even a 7 figure settlement (in extreme situations).
If You Have Any of the Symptoms Above, You Should Seek Immediate Medical Help
An undiagnosed and untreated brain injury can change your life forever. It is wise to seek medical care immediately to begin necessary treatment and avoid complications that could include lifelong disabilities.
Once you seek the care you need, consider connecting with an attorney who can help you decide whether you should pursue a legal case for compensation from the at-fault party for your injuries.










